Proof of the angle sum theorem
Angle sum theorem: The angle measures in any triangles add up to 180 degrees.
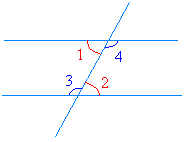
The figure above shows two pairs of alternate interior angles.
For the pair in red, angle 1 = angle 2. For the pair in blue, angle 3 = angle 4
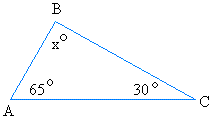
Now, take a close look at the figure below. I claim that angle x is equal to 85 degrees so the sum is 180 degrees.
To see why this is so, draw a line parallel to AC at vertex B
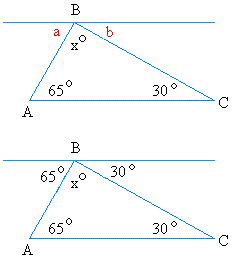
Angle a = 65 degrees because it alternates with the angle inside the triangle that measures 65 degrees
Angle b = 30 degrees because it alternates with the angle inside the triangle that measures 30 degrees
Looking at the figure again, it is easy to see why angle x is 85.
Since the 65 degrees angle, the angle x, and the 30 degrees angle make a straight line together, the sum must be 180 degrees
Since, 65 + angle x + 30 = 180, angle x must be 85
This is not a proof yet. This just shows that it works for one specific example
Proof of the angle sum theorem:
Start with the following triangle with arbitrary values for the angles:

angle a + angle b + angle c = 180 degrees
Since alternate interior angles are equal, angle a = angle x and angle b = angle y
Therefore, angle x + angle y + angle c = 180 degrees