Area of a kite
To find the area of a kite, we will use the kite below with a line of symmetry d1. Notice that when d1 is a line of symmetry, the kite is made of 2 congruent triangles.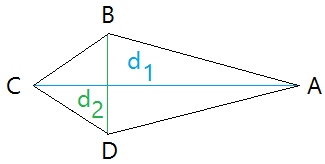 Kite
Kite
Area of kite = area of triangle ABC + area of triangle ADC
Be careful!
base = d1
base = d1
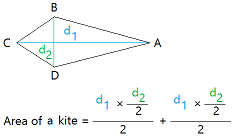
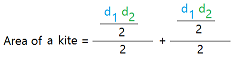
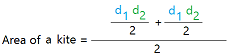
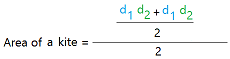
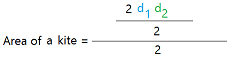
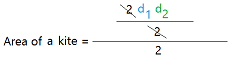
Here is the formula for the area of a kite using the diagonals.
Once you know the lengths of the diagonals, you can just multiply them and divide the result by 2.
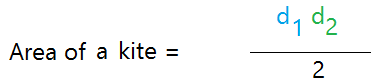
Example #1
Find the area of a kite with diagonals that are 6 inches and 18 inches long.
Area = (6 × 18) / 2 = 108 / 2 = 54 square inches.
Example #2
When the diagonals of a kite meet, they make 4 segments with lengths 6 meters, 4 meters, 5 meters, and 4 meters. What is the area of the resulting kite.
d2 = 4 + 4 = 8 meters
The segments with lengths 6 meters and 5 meters must represent d1 then
d1 = 6 meters + 5 meters = 11
Area = (8 × 11) / 2 = 88 / 2 = 44 square meters
Another formula for the area of a kite using trigonometry.
 Kite
KiteIf the unequal sides of a kite are known along with the included angle, the area of a kite is the product of the unequal sides and the sine of the included angle.
Area of the kite above = CB × AB × sin(B)
This concept is based on finding the area of a triangle given sas (side-angle-side).
For example, looking at the figure above, two unequal sides could be CB and AB. The angle between them is angle B.
The area of triangle ABC is 1/2[CB × AB × sin(B)]
Since diagonal d1 is a line of symmetry, triangle ADC and triangle ABC are congruent triangles.
Therefore, the area of triangle ADC is equal to the area of triangle ABC. The total area is found by adding the areas of the two triangles.
Area of the kite = area of triangle ABC + area of triangle ADC
Area of the kite = 1/2[CB × AB × sin(B)] + 1/2[CB × AB × sin(B)]
Area of the kite = [CB × AB × sin(B)] (1/2 + 1/2)
Area of the kite = [CB × AB × sin(B)] (1)
Area of the kite = [CB × AB × sin(B)]
Example #3
Suppose CB = 8 cm, AB = 15 cm, and angle B is 90 degrees. Find the area of the kite.
Area of the kite = [8 × 15 × sin(90 degrees)]
Area of the kite = [120 × sin(90 degrees)]
Area of the kite = (120 × 1)
Area of the kite = 120 cm2
Notice that in example #3, angle B and angle C are right angles. Therefore, this kite is made with two right triangles.
A rhombus is a kite made with two isosceles triangles.
Example #4
Find the area of the kite shown in the figure below which can also be called a rhombus.
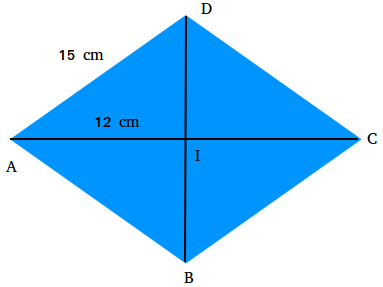
AD = 15 cm and AI = 12 cm
Use the Pythagorean theorem to find the length of segment DI
152 = 122 + DI2
225 = 144 + DI2
225 - 144 = 144 - 144 + DI2
225 - 144 = 144 - 144 + DI2
81 = DI2
9 = DI
Since the diagonals of a rhombus bisect each other, AC = 24 and DB = 18.
According to the formula, we know that the area is half the product of the lengths of its diagonals.
Area = 1/2(24 × 18)
Area = 1/2(432)
Area = 216 cm2