Base angles theorem
The base angles theorem states that if the sides of a triangle are congruent (Isosceles triangle)then the angles opposite these sides are congruent.Start with the following isosceles triangle. The two equal sides are shown with one red mark and the angles opposites to these sides are also shown in red.
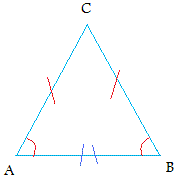
The strategy is to draw the perpendicular bisector from vertex C to segment AB
Then use SAS postulate to show that the two triangles formed are congruent
If the two triangles are congruent, then corresponding angles to will be congruent
Draw the perpendicular bisector from C
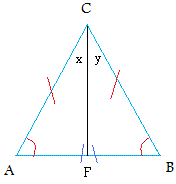
angle (x) = angle (y)
Segment AC = segment BC ( This one was given)
Segment CF = segment CF (Common side is the same for both triangle ACF and triangle BCF)
Triangles ACF and triangle BCF are then congruent by SAS or side-angle-side
In other words, by
AC-angle(x)-CF
and
BC-angle(y)-CF
Since triange ACF and triangle BCF are congruent, angle A = angle B
|
|
