Inverse proportion
In an inverse proportion, when one quantity increases by a certain factor, the other quantity decreases by the same factor. Keep reading to see a real-life example of this situation.
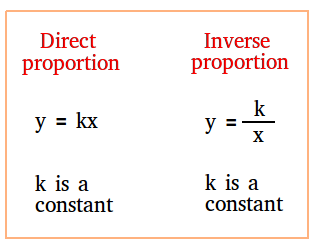
Suppose x and y are variables and k is a constant. Then, y = 8x and y = -2x are examples of direct proportions.
However, y = 3/x and y = -4/x are examples of inverse proportions.
A real life example of inverse proportion
A good real-life example of inverse proportion is the speed you drive and the time it takes to travel a certain distance. Suppose you need to drive to a city that is located 200 miles away.
The following table shows the time it will take you to get to your destination based on the speed.
| Speed (miles per hour) | Time |
| 20 m/h | 10 hours |
| 40 m/h | 5 hours |
| 80 m/h | 2.5 hours |
Did you make the following observations?
- 20 × 2 = 40 and 40 × 2 = 80
- 10 ÷ 2 = 5 and 5 ÷ 2 = 2.5
This means that every time you multiply the speed by 2, the time it takes to get to your destination is divided by 2 or multiplied by 1/2.
In general, with inverse proportion, when one quantity is multiplied by x, the other quantity is divided by x or multiplied by 1/x
Furthermore, notice the following:
20 × 10 = 200
40 × 5 = 200
80 × 2.5 = 200
200 is a constant, so let k = 200.
20, 40, or 80 is the independent variable, so let x = 20, 40, or 80
10, 5, or 2.5 is the dependent variable, so let y = 10, 5, or 2.5
We get x × y = 200 or y = 200/x
In general, with inverse proportion, y = k/x and we say that y is inversely proportional to x.
Other real-life examples of inverse proportion
- The number of people doing something and the time it takes to do it. As the number of people increases, the time it takes to finish decreases.
- Sharing a specific amount of money with a certain amount of people. As the number of people increases, the amount decreases.
- Suppose your income is constant. The money you save is inversely proportional to your expenses.
The figure below nicely summarizes the difference between direct proportion and inverse proportion