Parallel circuit rules
The parallel circuit rules show how to use Ohm's law when the circuit has more than one device receiving electrical energy. The rules will also help us see how the resistance, the current, and the voltage change in the parallel circuit.
Below is an example of a parallel circuit with 5 electrical components, excluding wires. The circuit has 2 switches (green), 1 voltage source of 24 volts, and 2 resistors.
In a parallel circuit, the current has more than 1 pathway.
To be more precise, the circuit below has 2 pathways.
Simply
put, the current has the ability to "make choices" as to where it would
go. If the current can either go this way or that way, then the circuit
is a parallel circuit. A circuit where electrons that cannot "make choices" as to how they will flow is a series connection.
Look carefully at the circuit below and you will see that the current can either go to the 8 Ohms resistor or the 4 Ohms resistor. This is what we mean by "making choices."
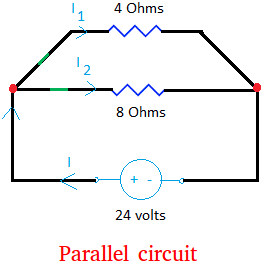
Take a close look at the two red dots. Did you notice that both resistors are connected to the same two red dots? This means that both resistors are
fed by the same voltage of 24 volts.
The red dots that you see are usually called nodes. However, this is not quite accurate. Nodes are entire section of wires where two or more things are connected.
For example, the 3 wires with the red dot binding them together is a node and this node connect two resistors and a voltage source! The above circuit has two nodes, one on the left and one on the right.
Rule #1: Devices in parallel circuits have the same voltage (or voltage drop) as the voltage source.
Let V1 be the voltage feeding the device with the 4 Ohms resistor.
Let V2 be the voltage feeding the device with 8 Ohms resistor.
Then, V = V1 = V2
Now, let us talk about the current. Let us pretend that the resistance is the same in both branches as shown in the circuit diagram below.
Since there is a resistance, the current going there will be less.
Since the resistance is the same for both branches, it makes sense to say that both branches will receive the same amount of current.
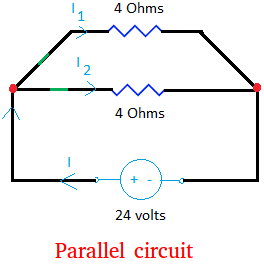
The total current I is split into I1 and I2. Half of the current will go to the branch with the 4 Ohms resistor and the other half to the branch with the 4 Ohms resistor.
If one resistor is equal to 4 Ohms and the other 8 Ohms like the first figure, more current will go to the branch with 4 Ohms. In fact twice as much current will go to the branch with a lesser resistance.
However, the amount of current that will go to the two branches must equal the amount that came from the source or the current I.
Rule #2: In parallel circuit, the current in the circuit is equal to the the sum of the currents in its parallel branches.
I = I1 + I2
Now we can find the resistance for the circuit using I = I1 + I2Let R1 and R2 be the resistances in the 2 branches. Let Rp be the resistance of the circuit. The resistance of the circuit is usually called equivalent resistance or total resistance. Ohm's law will apply separately to each branch.
I = I1 + I2
V/Rp = V/R1 + V/R2
V/Rp = V(1/R1 + 1/R2)
Divide both sides of the equation by V and you will end up with Rule #3
Rule #3:
|
1
Rp
|
=
1
R1
|
+
1
R2
|
|
1
Rp
|
=
1
R1
|
+
1
R2
|
Parallel circuit rules generalization
The parallel circuit rules can be summarized and generalized as shown below.
Let V be the voltage feeding the circuitLet V1, V2,..., Vn be the voltage feeding other devices in the branches
Then, V = V1 = V2 = ... = Vn
Let I be the current in the circuit
Let I1, I2,..., In be the current going to other devices in the branches
Then, I = I1 + I2 + ... + In
Let R1, R2, ... , Rn be the resistances in the branches. Let Rp be the equivalent resistance.
|
1
Rp
|
=
1
R1
|
+
1
R2
+ ...
|
+
1
Rn
|
Any questions about the parallel circuit rules? Send an email
Parallel circuit rules quiz
Take the parallel circuits quiz below to see how well you understand
parallel circuits. After completing this quiz with 100% accuracy, you
will know exactly how the current, the voltage, and the resistors behave
in a parallel circuit. You will not need to use a paper and pencil to
complete this quiz.
First, read the lesson about parallel circuits and then take this quiz.
Objective of the parallel circuit quiz:
- Know how the current behaves in a parallel circuit
- Know how the voltage behaves in a parallel circuit
- Know how the resistor behaves in a parallel circuit
- Know how to apply Ohm's law to find the current going through the circuit.
- Find the current in the circuit
|
Test your knowledge with the quiz below: |