Projectile word problems
A few carefully chosen projectile word problems to help you see how to solve these problems.
Problem #1:
A ball is dropped from a helicopter traveling with a speed of 75 m/s. After 2 seconds, the ball lands in the pool. Assuming no air resistance, what was the horizontal distance between the ball and the pool when it fell from the helicopter?
Solution
Key ideas
The first key idea here is that once released, the ball is a projectile launched horizontally.
Furthermore, since the ball was dropped and not shot from the helicopter, the ball will have the same velocity as the helicopter.
Finally, since the ball will travel horizontally, we can use the formula
distance = speed × time
distance = 75 m/s × 2 s = 150 meters
The helicopter was 150 meters away from the pool.
Interesting projectile word problems
Problem #2:
From a height of 5 meters, a ball is thrown horizontally a distance of 15 meters. What is the speed of the ball?
Use g = 10 m /s2Solution
We already have the distance the ball will travel. It is 15 meters. All
we need now is the time it takes the ball to hit the ground. Since the
ball is experiencing free fall before it hits the ground, we can use the
free fall equation.
The height the ball fell is 5 meters, so replace d with 5.
d = 5t25 = 5t2
5/5 = (5/5)t2
1 = 1t2
t = 1
The ball hit the floor after 1 second.
Speed = 15 m/s
Problem #3:
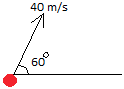
A projectile is launched with a speed of 40 m/s at 60 degrees above the horizontal. What are the horizontal and vertical velocities at launch?
Now we show the horizontal component in blue and the vertical component in green.
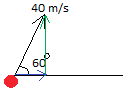
Some basic trigonometric identities will help us solve this now.
Let us call the horizontal speed vx and the vertical speed vyvx = 0.5 × 40 = 20 m/s
vx = 0.86 × 40 = 34.4 m/s