Proof of the area of a circle
Here is a proof of the area of a circle to satisfy the usual questions teachers get all the time when introducing the formula to find the area of a circle:
A = π × r2
We start our proof by having you look at the following figures:

Did you notice that as we went from 4 sides to 8 sides, the area outside the circle, but inside the square shrank considerably? This is illustrated below in brown.
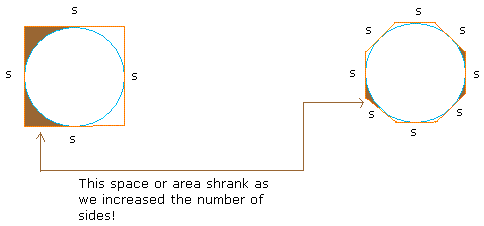
Now if we keep increasing the number of sides to a very very big number (call the resulting polygon an n-gon), this space will be so small, it will look like the circle is the same as the n-gon with a lot of sides.
Keep this fact in mind since we will refer back to it later!
Hang on buddy! We are halfway of completing the proof of the area of a circle. Now, consider the following octagon.
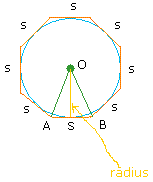
The area of triangle AOB is 1/2 ( base × height) = 1/2 (s × r)
We can make 8 such triangles inside the octagon as show below:
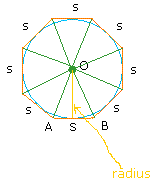
This means that the area of the entire octagon is 8 ×( 1/2 (s × r)) = 1/2 r × 8s
Notice that 8s is equal to the perimeter of the octagon.
As stated before, if we increase the number of sides to infinity or a very big number, the resulting n-gon ( The regular polygon which number of sides is a big number) will almost look like a circle.
This means that the perimeter of the resulting n-gon will almost be the same as the perimeter of the circle.
As a result, the closer the perimeter of the polygon is to the circle, the closer the area of the polygon is to the area of the circle.
It is reasonable then to replace 8s by 2 × pi × r, which is the perimeter of the circle, to calculate the area of the polygon or the circle when the number of sides is very big.
Doing so we get:
Area of circle or polygon equal = 1/2 r × 2 × pi × r = pi × r2
Proof of the area of the circle has come to completion. Any questions? Contact me