Ratios
The objective of this lesson is to define what a ratio is and show you how to write ratios using some situations or examples you encounter daily. We will also provide you with a definition of continued ratio. Finally, we will show you some common pitfalls to avoid when working with ratios.Start exploring ratios with the interactive practice below.
Understanding Ratios
Things are not always the same size. Thus, a natural need arise to compare quantities using division to see how much bigger a quantity is when compared to another.
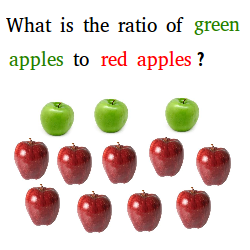
For example, looking at the two piles above made of red apples and green apples, you may not be satisfied just to know that there are more red apples.
A comparison of red apples to green apples using division is a ratio and this comparison may help you to see how much more red apples there are.
9 3 = 3
The quotient or answer to the ratio above is equal to 3 and we can quite interpret the answer.
It means that there are 3 times more red apples than green apples.
Other Real-Life Examples of Ratios
Say for instance, you are in a classroom. In the classroom, there are 3 boys and 6 girls.The ratio of boys to girls is 3 6 = 1 2 or 0.5
It means that there are half as many boys as girls in the classroom.
You can also do the following ratios:
Ratio of boys to number of students in the classroom: 3 9
Ratio of number of students in the classroom to girls: 9 6
Ratio of number of students in the classroom to boys: 9 3
At this point you may have noticed that the order is important when defining a ratio. The number that comes after ' of ' is your numerator and the number that comes after ' to ' is your denominator.
Some Formal Definitions of Ratios
A ratio is a comparison of two numbers using division.The ratio of a to b is a b with b ≠ 0
A ratio is an ordered pair of numbers, written a:b, with b ≠ 0
As you can see there are more than one way to express a ratio. For example, if you have 6 pencils and 2 pens all the followings are good ways to express the ratio of pens to pencils.
2:6
2 6
The word "per" also means a ratio
For example, gas mileage such as 50 miles per 4 gallons means 50 4
Wage such as 25 dollars per hour means 25 1
What is a Continued Ratio? Definition and Examples
The ratio of three or more quantities is called continued ratio. For example, the ratio of 4 to 8 to 12 is the continued ratio 4:8:12.
We get the continued ratio above by combining the following 3 ratios:
4:8, 8:12, and 4:12
An Important Thing to Keep in Mind When Working with Ratios
When doing ratios, make sure that quantities are in the same units first.Ratio of 24 inches to 6 feet
Since 1 foot = 12 inches, 6 feet = 6 × 12 inches = 72 inches.
Now, you can do the ratio of 24 inches to 72 inches.
24 72
It may be useful to simplify a ratio sometimes such as the one immediately above.
Just divide both numerator and the denominator by the greatest common factor.
24 ÷ 24 72 ÷ 24
We get: 1 3
Here is a little interesting word problem about ratios.
A classroom has 50 students and the ratio of males to females is 2 to 3. How many students are females? How many students are males
2 to 3 is the same thing as 20 to 30
20 + 30 = 50
Therefore, there are 30 females and 20 males in this class.
Are Ratios the Same as Fractions?
The short answer is no, not exactly. Although, there a small similarity, there is still a big difference between ratios and fractions. You can read this lesson to fully understand the difference a ratio and a fraction.