Trigonometric ratios
Here we will show you the six trigonometric ratios. They are used only for triangles that have a right angle.
If the triangle is not a right triangle, none of the formulas shown below are valid. It is extremely important to keep this in mind.
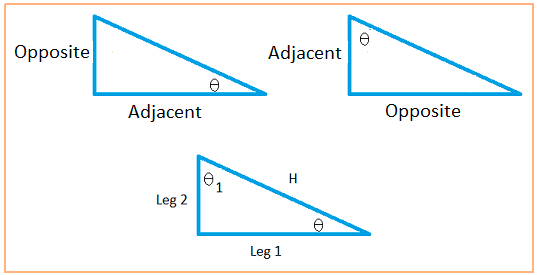
Here are the six trigonometric ratios using θ as the angle
Sine ratio
Cosine ratio
Tangent ratio
Cotangent ratio
Secant ratio
Cosecant ratio
Here are the six trigonometric ratios using θ1 as an angle

Sine ratio
Cosine ratio
Tangent ratio
Cotangent ratio
Secant ratio
Cosecant ratio
Important observations about the six trigonometric ratios
- The tangent is the ratio of the sine to the cosine.
- The cotangent is the inverse of the tangent.
- The cosecant is the inverse of the sine.
- The secant is the inverse of the cosine.
A triangle is a right triangle if one of the angles is equal to 90 degrees. First make sure you examine the three right triangles in the diagram above so you understand what the opposite and adjacent sides are.
Notice that the hypotenuse is the line that is neither vertical nor horizontal.
The two triangles on top do not have any label on the triangles to identify the hypotenuse. However, the hypotenuse is the line that is slanted.
Remember that an angle is made with two sides. The side that is opposite to the angle θ is the side that is not used to create the angle. I hope this helps to identify the opposite side.
The adjacent side is one of the sides that is used to make the angle, but it is not the hypotenuse or the slanted side.
The adjacent side is going to be either the horizontal side or the vertical side.